|
Discovery Toxicity study |
Target Organ Toxicity Evaluation |
|
Mechanistic toxicity study |
Study of how chemical or physical agents interact with living organisms to cause toxicity |
|
Genotoxicity study |
Comet assay and result analysis methodology |
|
Cardiovascular toxicity study |
Assessment of telemetry systems in beagle dogs |
|
Tissue Cross Reactivity (TCR) study |
Evaluation by IHC in laboratory animals and human tissues |
|
Combined exploratory toxicity study |
Simultaneous DRF, target toxicity exploration, PK/PD, cardiovascular toxicity evaluation, and comet assay in Rodent/Dog Models |
Service
- Conduct non-clinical studies through combined exploratory toxicity studies.
- Provide toxicity interpretation services for Go/No-Go decision-making based on GLP-level preliminary safety evaluation.
- Assess potential genotoxicity through the Comet assay.
- Evaluate potential cardiovascular toxicity using a telemetry system.
- Perform ocular toxicity assessments using techniques such as Schirmer’s test, fundus camera, and OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) across rodent to primate models.
- Identify cross-reactivity of antibody-drugs and determine On-target/Off-target antigen binding sites in tissues from both laboratory animals and humans using immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Pursue broader assessments of the human relevance of toxicity through investigative toxicology.

Combined exploratory toxicity
study in rodents
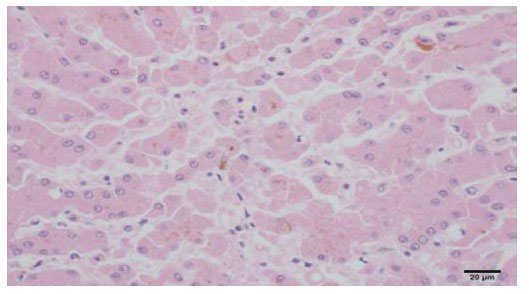
Histopathological finding
(Cholestasis, dog, liver, H&E, x400)
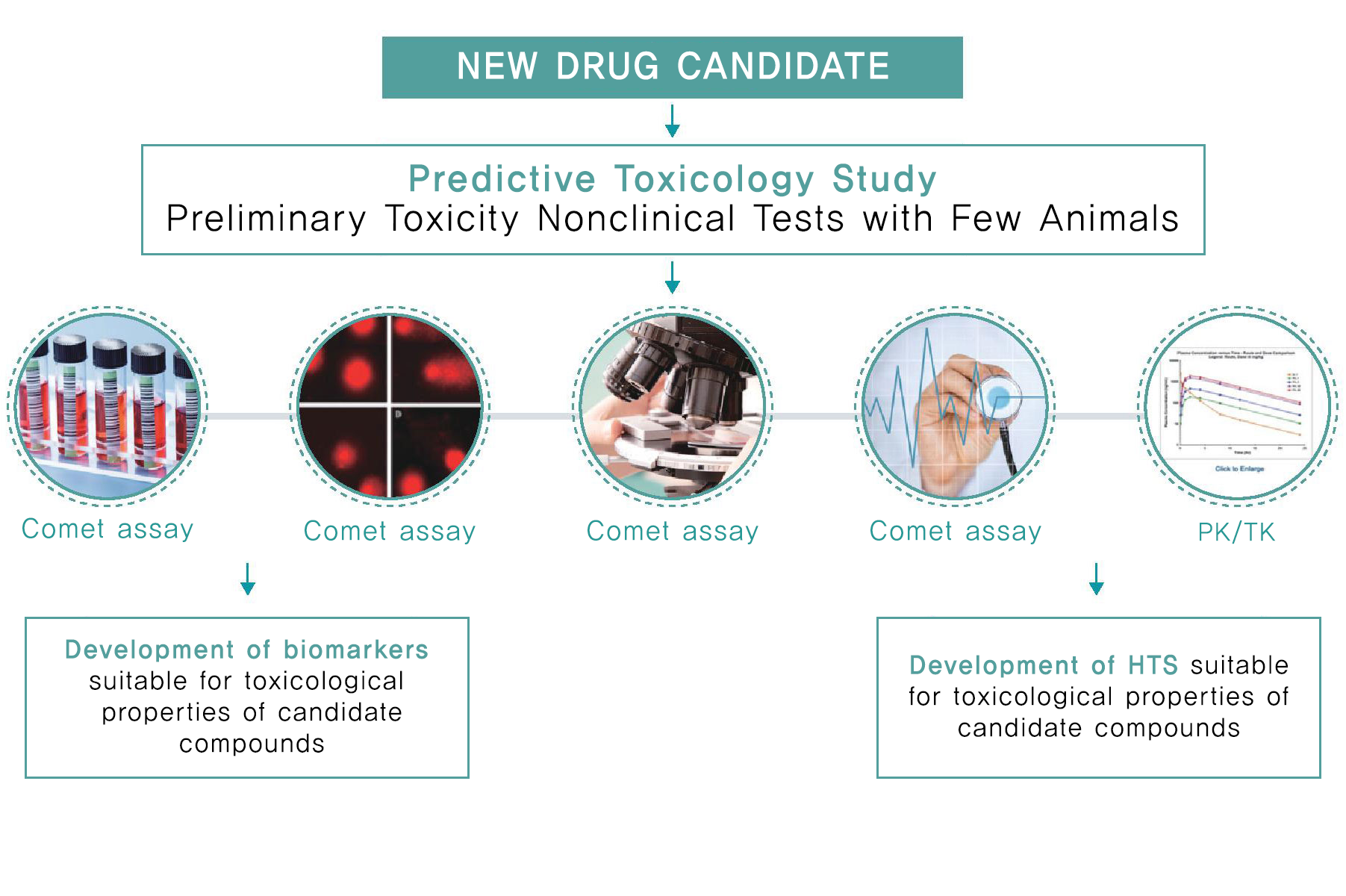
Service example ( Rodent Toxicity Assessment)
- Combined exploratory toxicity study in rodents for drug development
|
Overview |
A Dose Range Finding (DRF) study was conducted in ICR mice to determine the appropriate dosing range of the investigational drug for toxicity testing |
|
Design |
- Based on DRF results, dose levels of 60 mpk, 180 mpk, and 540 mpk were established. - A 2-week repeat-dose toxicity study was performed in ICR mice using the selected dose levels. - During necropsy, liver and bone marrow tissues were collected, and an in vivo Comet assay was performed. - Histopathological examination was conducted to assess target organs. |
|
Result |
- At high doses, weight loss and signs of reduced vitality were observed. 
Liver, control 
Liver, treated Comet assay results show potential genotoxicity |
Service example ( beagle dog toxicity evaluation)
- Combined exploratory toxicity study in beagle dogs for drug development
|
Overview |
A dose-escalation study followed by a repeated-dose toxicity study was conducted in beagle dogs to evaluate the selected doses. |
|
Design |
- A dose-escalation study was first conducted in one male and one female beagle dog. Based on the results, the dose for the repeated-dose study was set at 400 mg/kg. - A 2-week repeated-dose toxicity study was then carried out using the selected dose. - Throughout the study, body weight and clinical symptoms were monitored. - Telemetry measurements were taken at the first dose, one week after dosing, and on the final day to evaluate cardiovascular toxicity. - Hematological and serum biochemical tests were performed through blood collection, and toxicokinetic (TK) analysis was conducted. |
|
Result |
- Organ histopathological examination results: Lesions caused by the drug were observed in the liver, kidneys, lungs, and small intestine. - Comet assay results: No DNA damage caused by the drug was observed. - Telemetry analysis: No cardiovascular toxicity was observed. - Maximum Tolerated Dose (MTD): Determined to be 400 mg/kg or less. 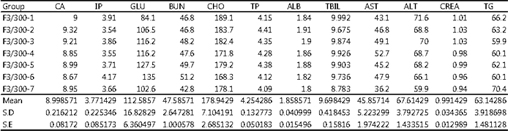
Results of performing serum biochemical tests 
Histopathological findings (Cholestasis, dog, liver, H&E, x 400) |





